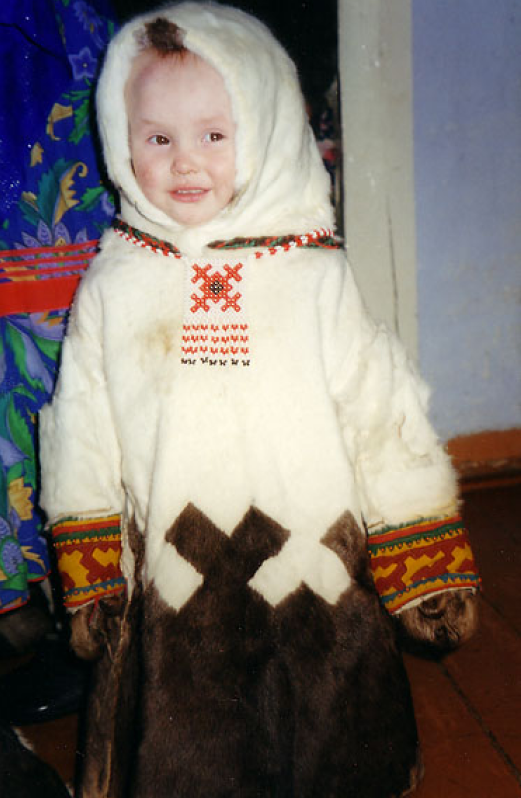
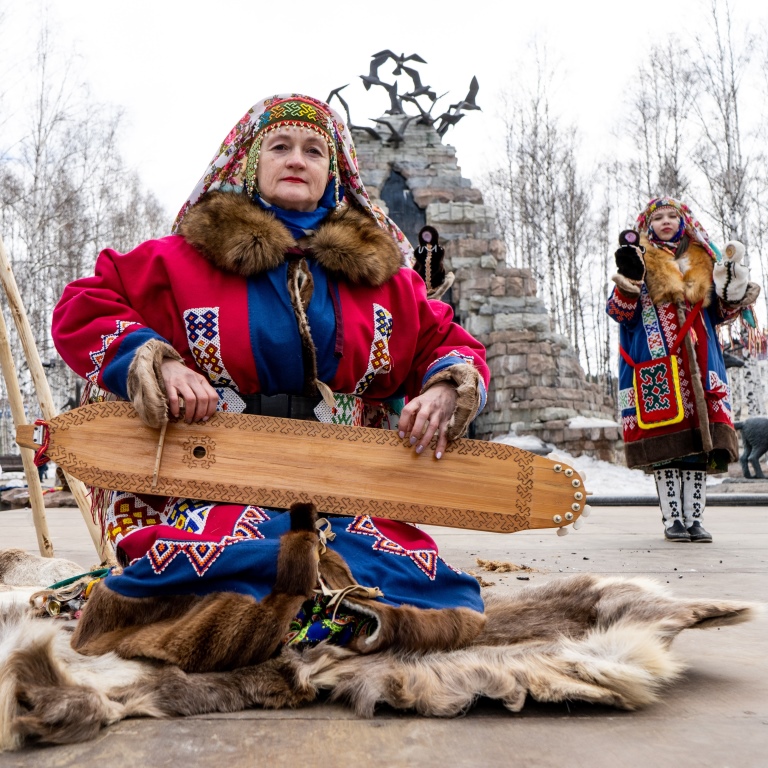
Народы и языки
Образовательные практики
Новости
Виртуальные экскурсии
Память Победы
Стипендиаты именных стипендий для КМНС
Молодость Севера
Сокровища Cевера
Современные исследования о коренных малочисленных народах
Законодательство, регулирующее права коренных малочисленных народов
SNOWORD
Север в лицах
Как Россия осваивала Сибирь,
Арктику и Дальний Восток Литература о народах Севера Отзывы об Интерактивном атласе
Арктику и Дальний Восток Литература о народах Севера Отзывы об Интерактивном атласе
Социальные сети
Оставляйте комментарии, предложения, следите за новостями в наших группах в ВК, Одноклассниках и Telegram канале.